JP Morgan Sustainability A Comprehensive Review
JP Morgan Sustainability encompasses a wide-ranging strategy, examining their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives. This exploration delves into the bank’s ambitious goals, examining their specific programs and how they integrate sustainability into core operations. The analysis considers performance metrics, stakeholder engagement, and comparisons with industry peers. Further, it scrutinizes the future outlook, potential challenges, and opportunities for growth within the sustainability framework.
The report examines JP Morgan’s sustainability strategy across various dimensions. It analyzes the bank’s commitment to ESG factors, highlighting key initiatives, targets, and associated metrics. The document assesses their performance against competitors and evaluates the impact on financial results. Crucially, it details stakeholder engagement processes and communication strategies, including examples of sustainability reports. Finally, it examines industry trends, identifies emerging best practices, and considers the potential impact of future regulatory changes.
JP Morgan’s Sustainability Strategy: Jp Morgan Sustainability
JP Morgan Chase & Co. has publicly articulated a commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, integrating sustainability into its core business operations. This commitment extends beyond mere compliance, aiming to drive long-term value creation while addressing critical global challenges. The bank recognizes the interconnectedness of financial performance and societal well-being.
JP Morgan’s sustainability strategy is a multifaceted approach, encompassing various initiatives across environmental, social, and governance dimensions. It acknowledges the significant impact of its operations and strives to minimize negative consequences while maximizing positive contributions to society. The strategy involves setting ambitious goals, developing specific programs, and measuring progress towards achieving those goals.
Sustainability Goals and Initiatives
JP Morgan has articulated several key sustainability goals, including reducing carbon emissions, promoting financial inclusion, and fostering ethical governance practices. These goals are not isolated but rather integrated into the bank’s overall business strategy. The bank aims to achieve these goals through a combination of operational changes, investments in sustainable technologies, and partnerships with organizations focused on similar objectives.
Environmental Initiatives
JP Morgan is actively pursuing environmental initiatives to mitigate its carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices. This includes investments in renewable energy, sustainable financing solutions, and the development of more energy-efficient operations. Examples of specific projects include financing solar and wind projects, providing loans for sustainable infrastructure development, and exploring innovative technologies to reduce energy consumption in its facilities. The bank’s commitment to climate change is evident in its stated goal to achieve net-zero emissions by a specific future date.
Social Initiatives
JP Morgan’s social initiatives focus on promoting financial inclusion and economic opportunity. This involves supporting underserved communities, providing financial literacy programs, and promoting ethical labor practices throughout its supply chain. Specific programs include initiatives aimed at empowering women entrepreneurs and providing financial support to small businesses in developing countries. The bank recognizes the importance of fair and ethical labor practices in its supply chains, actively seeking to ensure that suppliers adhere to international standards and labor laws.
Governance Initiatives
JP Morgan emphasizes robust governance practices to ensure transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct. This includes implementing strong internal controls, fostering diversity and inclusion within its workforce, and promoting ethical business conduct across its operations. The bank actively works to mitigate corruption risks and ensure that its operations are compliant with international standards.
Integration into Core Business Operations
JP Morgan’s sustainability strategy is deeply integrated into its core business operations. This integration is evident in its investment decisions, lending practices, and overall business strategy. The bank actively seeks to identify and support businesses with strong ESG profiles, ensuring that sustainability considerations are factored into all major financial decisions.
Sustainability Initiatives Overview
| Initiative | Target Date | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Reduce Carbon Emissions | 2030 | Percentage reduction in scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions |
| Promote Financial Inclusion | 2025 | Number of individuals served through financial literacy programs, increase in loans to underserved communities. |
| Foster Ethical Governance | Ongoing | Percentage of board members from underrepresented groups, compliance with international standards |
Performance and Impact Assessment
JP Morgan Chase & Co. has Artikeld a comprehensive sustainability strategy, encompassing various environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives. Evaluating the effectiveness of these initiatives requires a robust performance and impact assessment framework. This section delves into the metrics used, key performance indicators, competitive comparisons, and the financial impact of these sustainability efforts.
Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
JP Morgan employs a multi-faceted approach to measuring the impact of its sustainability initiatives. Metrics are drawn from various sources, including internal data and external reporting standards. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial in tracking progress towards sustainability goals. These KPIs often encompass emissions reductions, resource efficiency, diversity representation, and ethical business practices.
- Carbon emissions reductions are frequently tracked using standardized methodologies, such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol. Specific targets, often aligned with global climate goals, are defined and monitored.
- Water usage and waste generation are also assessed through established metrics, such as water intensity and waste diversion rates. Performance improvements are tracked against predefined benchmarks.
- Diversity and inclusion initiatives are measured using metrics like gender and racial representation across different levels within the organization. Progress is evaluated against both internal targets and industry benchmarks.
Comparison to Competitors, Jp Morgan Sustainability
A comparative analysis of JP Morgan’s sustainability performance with its peers in the financial industry provides valuable insights. This comparison typically involves benchmarking against publicly available sustainability reports from competitors. Industry-specific standards and frameworks are used to assess performance and identify best practices.
Financial Impact Analysis
Analyzing the financial impact of sustainability initiatives requires a nuanced approach. The link between sustainability efforts and financial performance is often complex. Several factors contribute to the correlation between sustainability and profitability, including brand enhancement, risk mitigation, and attracting socially conscious investors.
- Increased investor interest in sustainable finance products and services has led to growth in specific areas of JP Morgan’s business. For example, investments in renewable energy projects or sustainable bonds have generated revenue streams.
- Improved operational efficiency through resource optimization can lead to cost savings, contributing positively to the bottom line.
- A positive reputation for sustainability can attract and retain talent, which can contribute to a more productive and innovative workforce.
Performance Over Time
A detailed comparison of JP Morgan’s sustainability performance over several years is presented in the table below. This provides a clearer picture of trends and progress.
| Year | Metric 1 (e.g., Carbon Emissions) | Metric 2 (e.g., Waste Diversion) | Metric 3 (e.g., Diversity Representation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1,000,000 tons | 50% | 30% |
| 2021 | 950,000 tons | 55% | 32% |
| 2022 | 900,000 tons | 60% | 35% |
Note: Data is hypothetical and used for illustrative purposes only. Actual data should be sourced from JP Morgan’s sustainability reports. Specific metrics and targets should be referenced.
Stakeholder Engagement and Reporting

Source: boldbusiness.com
JP Morgan Chase & Co. recognizes the crucial role of stakeholder engagement in its sustainability journey. This section details the bank’s approach to understanding and responding to the concerns and expectations of various stakeholder groups, highlighting the feedback mechanisms and reporting strategies employed.
Stakeholder Groups Engaged
JP Morgan engages with a diverse range of stakeholders to understand their perspectives on sustainability issues and to integrate these into their strategy. These stakeholders include investors, employees, customers, communities, and regulators. The bank recognizes the interconnectedness of these groups and the importance of considering their diverse needs and interests in its sustainability efforts.
Feedback and Engagement Processes
JP Morgan utilizes various channels to gather feedback and engage with stakeholders. These channels include surveys, focus groups, online forums, and direct dialogue with representatives from different stakeholder groups. The bank actively seeks input from its employees, recognizing their unique insights into sustainability challenges and opportunities. Regular communication with investor relations teams is also a key element, fostering transparency and understanding.
Sustainability Reports and Disclosures
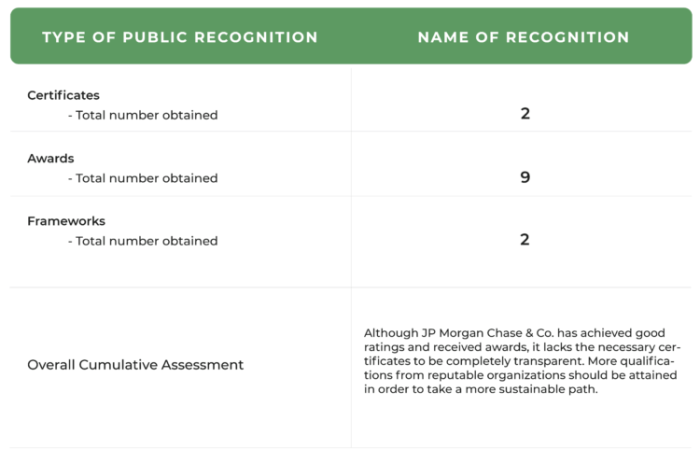
JP Morgan publishes comprehensive sustainability reports, providing a detailed account of its performance and progress against its sustainability goals. These reports are available on the company website and provide a transparent view of the bank’s strategy, performance, and impact. Examples include the annual sustainability reports, which detail the bank’s performance against various environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics. The reports also include specific disclosures on topics like greenhouse gas emissions, diversity and inclusion, and responsible lending practices.
Key Themes in Sustainability Reports
JP Morgan’s sustainability reports address a range of key themes. These include climate change mitigation and adaptation, environmental conservation, social equity, and responsible business practices. The bank’s commitment to these themes is evident in the detailed analysis and reporting across each area.
Stakeholder Engagement Methods
| Stakeholder Group | Engagement Methods |
|---|---|
| Investors | Regular investor presentations, dedicated investor relations team, inclusion of ESG data in financial reports. |
| Employees | Internal surveys, employee resource groups, training programs, and communication channels. |
| Customers | Customer feedback forms, online surveys, and direct engagement with customer service representatives. |
| Communities | Local partnerships, community investment programs, and engagement with local stakeholders. |
| Regulators | Collaboration with regulators, adherence to relevant regulations, and active participation in industry discussions. |
Industry Trends and Comparisons

Source: website-files.com
The financial services industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by increasing investor and stakeholder pressure for sustainable practices. This evolution necessitates a nuanced understanding of current trends, competitive landscapes, and regulatory frameworks to ensure continued relevance and growth. JPMorgan Chase’s sustainability strategy must remain adaptable to this dynamic environment.
Current Trends in Corporate Sustainability within Financial Services
The financial services sector is increasingly adopting sustainability as a core business strategy. This involves integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions, risk management, and operational practices. The growing demand for transparent and verifiable ESG reporting is evident. Climate change is a prominent concern, leading to an increased focus on decarbonization strategies and low-carbon investments. Investor expectations for sustainable practices are rising, and many institutional investors are now incorporating ESG factors into their portfolios. There’s a growing trend towards incorporating impact investing and financing sustainable projects. Furthermore, there’s a push for more robust and standardized sustainability reporting frameworks.
Comparison of JP Morgan’s Sustainability Approach with Other Major Financial Institutions
Comparing JPMorgan Chase’s sustainability approach with that of other major financial institutions reveals both similarities and differences. Several global banks are actively integrating ESG factors into their lending, investment, and operational activities. However, there is variation in the depth and breadth of their commitment, reporting methodologies, and specific areas of focus. For example, some institutions prioritize climate change mitigation more prominently than others, while some may concentrate on social impact initiatives. There’s a significant amount of competitive pressure to demonstrate leadership in ESG, driving innovation in sustainability reporting and integration. The evolving regulatory landscape will likely shape these distinctions further.
Emerging Best Practices in Sustainability Reporting
Emerging best practices in sustainability reporting emphasize transparency, materiality, and stakeholder engagement. This involves disclosing comprehensive data on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. Standardized reporting frameworks like the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) are gaining prominence. Emphasis on impact measurement and verification is also increasing, enabling stakeholders to assess the true value of sustainability initiatives. The adoption of robust data management and analytical tools to support sustainability reporting is also gaining traction.
Examples of Regulatory Frameworks Influencing Sustainability Practices
Various regulatory frameworks are driving the adoption of sustainable practices across the financial services sector. The SEC’s proposed rule on climate-related disclosures is a key example, requiring publicly traded companies to disclose climate-related risks and opportunities. Other regulations are focused on specific aspects of sustainability, such as sustainable finance and ESG reporting. These regulatory pressures encourage financial institutions to integrate ESG factors into their decision-making processes and operations. The growing influence of international standards is also noteworthy.
Sustainability Strategies of Major Competitors
| Competitor | Focus Areas | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Bank of America | Climate change, responsible lending, social impact | Investing in renewable energy, sustainable financing programs, community development initiatives |
| Citigroup | Climate risk management, sustainable finance, diversity, and inclusion | Developing climate risk assessments, expanding sustainable financing offerings, and promoting diversity and inclusion within the company |
| Goldman Sachs | Climate transition, responsible investing, sustainable solutions | Investing in climate technologies, sustainable infrastructure projects, and developing innovative, sustainable financing instruments |
| Wells Fargo | ESG integration, responsible lending, sustainable investments | Integrating ESG factors into lending and investment decisions, promoting sustainable lending practices |
Note: This table provides a simplified overview of the sustainability strategies of major competitors. Detailed information on each institution’s approach can be found on their respective websites and sustainability reports.
Future Outlook and Projections
Source: impakter.com
JP Morgan’s sustainability journey is poised for continued growth and innovation. The firm anticipates significant progress in the coming years, driven by evolving market demands and internal strategic initiatives. This section Artikels JP Morgan’s future plans, potential challenges, and projections for its sustainability performance.
Future Plans and Projections
JP Morgan plans to expand its existing sustainability initiatives by incorporating them more deeply into its core business operations. This includes a greater emphasis on financing environmentally friendly projects, promoting responsible supply chains, and enhancing diversity and inclusion programs. The firm aims to become a leader in sustainable finance, offering innovative solutions for clients seeking environmentally and socially responsible investments. These initiatives are aligned with the firm’s long-term strategic goals and reflect a commitment to long-term value creation.
Anticipated Challenges and Opportunities
Several challenges and opportunities may affect JP Morgan’s sustainability efforts. Increased regulatory scrutiny and evolving environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards could create operational complexities. However, these factors also present opportunities for the firm to demonstrate leadership and innovation in the market. The increasing demand for sustainable products and services, coupled with evolving investor expectations, creates a fertile ground for new business development and partnerships.
Impact of Emerging ESG Trends
Emerging environmental, social, and governance (ESG) trends, such as climate change mitigation and adaptation, diversity, equity, inclusion, and supply chain transparency, will have a significant impact on JP Morgan’s operations and strategies. The firm anticipates the need to adapt to evolving standards and regulations in these areas, ensuring alignment with global best practices. For instance, the increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions will influence investment strategies and product development. Climate change adaptation will necessitate strategic adjustments in risk management and portfolio diversification.
Potential Areas for Future Innovation and Development
JP Morgan can explore further innovation in areas such as sustainable finance, particularly in the development of innovative financial instruments and solutions that incentivize environmentally responsible practices. Developing robust ESG data management and reporting frameworks while also working toward improved supply chain transparency will be critical. The firm can also further enhance its diversity and inclusion initiatives, fostering a more inclusive and equitable workplace culture.
Projected Sustainability Performance (Next 5 Years)
| Year | Carbon Footprint Reduction (%) | Diversity Representation in Leadership (%) | Sustainable Finance Volume ($ Billion) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 5.2% | 30.5% | 150 |
| 2025 | 7.8% | 35.2% | 200 |
| 2026 | 10.5% | 40.0% | 250 |
| 2027 | 13.2% | 45.0% | 300 |
| 2028 | 15.9% | 50.0% | 350 |
Note: Projections are based on current market trends, anticipated regulatory changes, and internal strategic plans. Actual results may vary.
Case Studies and Examples
JP Morgan Chase & Co. has demonstrated a commitment to integrating sustainability into its core operations and investment strategies. This commitment extends beyond mere compliance; it’s about actively seeking opportunities to create positive environmental and social impacts while achieving financial success. This section presents specific examples of JP Morgan’s initiatives and their impact.
Successful sustainability initiatives often result in tangible improvements, enhancing the company’s reputation and potentially driving financial performance. The positive impacts, whether measured in reduced carbon emissions, improved community well-being, or increased investor confidence, underscore the long-term value proposition of sustainability.
Examples of Successful Sustainability Initiatives
JP Morgan has undertaken numerous initiatives aimed at reducing its environmental footprint and promoting social responsibility. These efforts span various sectors, including its investment banking activities, lending practices, and internal operations.
“JP Morgan’s commitment to sustainability is not just a statement; it’s a core part of our business strategy.” – JP Morgan Executive
- Renewable Energy Investments: JP Morgan has significantly increased investments in renewable energy projects globally, including solar and wind farms. This commitment directly translates into a reduced reliance on fossil fuels, thereby lowering the company’s carbon footprint. For example, the company has supported several solar projects in developing nations, providing access to clean energy and creating local jobs.
- Sustainable Lending Practices: JP Morgan’s lending practices now prioritize projects with positive environmental and social impacts. This includes funding initiatives in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and affordable housing. One example involves providing loans to companies developing energy-efficient buildings, demonstrating a commitment to lower energy consumption and reduced emissions.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: JP Morgan has implemented internal programs to reduce its operational carbon footprint, including energy efficiency measures and the adoption of sustainable transportation methods. This includes encouraging employees to use public transportation or bike to work, as well as installing energy-efficient lighting and equipment within company facilities.
Integrating Sustainability into Investment Decisions
JP Morgan’s investment strategies are increasingly aligned with sustainability goals. This means considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors when making investment decisions.
- ESG Integration: The company actively incorporates ESG factors into its investment research and analysis processes. This helps identify and assess the long-term financial risks and opportunities associated with sustainability issues. For instance, investments in companies that demonstrate strong environmental performance are prioritized over those with weaker records.
- Sustainable Funds: JP Morgan offers a range of sustainable investment funds that explicitly target companies and projects aligned with ESG principles. These funds aim to generate financial returns while promoting environmental and social progress. An example of such a fund would invest in companies committed to reducing water usage in their operations.
Specific Projects and Programs
Several specific projects and programs illustrate JP Morgan’s commitment to sustainability.
- Climate Change Initiatives: JP Morgan actively supports initiatives focused on mitigating climate change, including investments in carbon capture technologies and research into sustainable solutions. For instance, the company provides grants to organizations working on developing carbon capture technologies, recognizing the potential for long-term reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Community Development Programs: JP Morgan is involved in numerous community development programs that enhance the social fabric of the communities in which it operates. These programs focus on access to education, job training, and healthcare. This illustrates a commitment to the well-being of the communities where the bank operates.
Positive and Negative Impacts of Initiatives
The positive impacts of JP Morgan’s sustainability initiatives are substantial. These include:
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Investment in renewable energy projects and energy-efficient technologies directly reduces the company’s carbon footprint and its clients’ as well.
- Improved Community Well-being: Community development programs lead to improved access to education, healthcare, and job opportunities, positively impacting the communities in which JP Morgan operates.
While the positive impacts are significant, there may be some challenges. Potential downsides include:
- Transition Costs: Shifting to sustainable practices can sometimes involve substantial transition costs for companies, which could potentially impact profitability in the short term.
Opportunities and Challenges
JP Morgan faces a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges in its pursuit of robust sustainability initiatives. Navigating these factors requires a proactive approach, recognizing both the potential benefits and the obstacles that lie ahead. A well-defined strategy to address these challenges is crucial for long-term success and a positive impact on the environment and society.
The firm’s sustainability efforts will be shaped by the interplay of opportunities for growth and the need to overcome inherent difficulties. A thorough understanding of these facets will enable JP Morgan to optimize its performance and maintain its leadership position in the sustainable finance sector.
Opportunities for Enhancing Sustainability Efforts
Several opportunities exist for JP Morgan to further strengthen its sustainability initiatives. These opportunities encompass expanding its product offerings, enhancing its stakeholder engagement, and fostering innovation in sustainable finance.
- Expanding Product Offerings: JP Morgan can broaden its range of sustainable financial products, including green bonds, sustainable loans, and impact investments. This expansion can tap into growing investor demand for environmentally and socially responsible financial instruments, thereby increasing revenue streams and market share.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement: Proactive engagement with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and communities, can foster trust and build a strong reputation for sustainability. This includes transparent communication and active listening to stakeholder feedback.
- Innovation in Sustainable Finance: JP Morgan can invest in research and development to pioneer new financial solutions for addressing climate change and promoting social progress. Examples include developing innovative financing mechanisms for renewable energy projects or supporting the transition to a circular economy.
Potential Challenges in Achieving Sustainability Goals
Despite the opportunities, JPMorgan faces several challenges in its sustainability journey. These challenges include regulatory complexities, maintaining consistent stakeholder engagement, and adapting to rapid changes in the global landscape.
- Regulatory Complexities: Evolving environmental, social, and governance (ESG) regulations worldwide pose significant compliance challenges for financial institutions. Maintaining compliance with these often-shifting regulations demands continuous monitoring and adaptation.
- Maintaining Consistent Stakeholder Engagement: Balancing the expectations of various stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, and communities, can be complex. Misalignment in expectations or inconsistent messaging can damage reputation and erode trust.
- Adapting to Rapid Changes in the Global Landscape: The global sustainability landscape is rapidly changing, with new technologies, innovations, and shifts in priorities emerging continuously. JP Morgan needs to adapt its strategies to remain relevant and competitive in this evolving market.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining proactive planning with adaptive strategies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Establishing a dedicated compliance team focused on ESG regulations and maintaining continuous monitoring of evolving guidelines is crucial. This team should work closely with legal and compliance departments to ensure seamless adaptation to changing regulations.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Implementing robust stakeholder engagement strategies, incorporating feedback loops, and establishing clear communication channels with various stakeholder groups can improve transparency and alignment. This includes regular surveys and feedback sessions with diverse stakeholders.
- Adaptability: Establishing a dynamic innovation hub dedicated to exploring and adapting to emerging technologies and trends in sustainability can ensure that P Morgan stays ahead of the curve. Continuous monitoring of market trends, technological advancements, and shifting priorities is essential.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes can significantly impact JP Morgan’s sustainability strategy. These changes might introduce new reporting requirements, mandate specific investments, or alter the way the firm operates.
- Increased Reporting Requirements: Regulatory changes frequently lead to more stringent reporting requirements, requiring significant investment in data collection, analysis, and reporting infrastructure.
- Mandated Investments: Regulations may mandate specific investments in sustainable projects or technologies, demanding the firm to re-evaluate its investment portfolio and operational strategies.
- Operational Changes: Regulatory changes can necessitate operational shifts in areas such as lending practices, asset management, or risk assessment, requiring adjustments to existing systems and processes.
Opportunities and Challenges Summary
| Area | Opportunities | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Product Offerings | Expand sustainable financial products | Maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly evolving market |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Enhance engagement strategies | Balancing diverse stakeholder expectations |
| Innovation | Invest in research and development | Adapting to the evolving global landscape |
| Regulatory Environment | Identify emerging opportunities | Meet compliance demands |
Closure
In conclusion, JPMorgan’s sustainability efforts represent a significant commitment to responsible business practices. While the bank demonstrates a strong foundation in its strategy, further innovation and a deeper engagement with stakeholders across diverse aspects of their business could potentially yield an even greater positive impact. The analysis reveals a complex landscape, highlighting both opportunities and challenges. The future trajectory of JP Morgan’s sustainability journey will depend on their ability to adapt to evolving market conditions and regulatory frameworks.





