CIAM Architecture A Comprehensive Guide
CIAM architecture provides a robust framework for managing user identities and access, essential for modern organizations. It encompasses various components, including identity management, access control, and authentication. Different deployment models, from cloud-based to on-premises solutions, offer diverse tradeoffs in scalability, security, and cost. This guide explores the key features, benefits, use cases, technical aspects, security considerations, and future trends of CIAM architecture.
This comprehensive overview delves into the intricacies of CIAM, detailing its core components and functionalities. We’ll explore the diverse types of CIAM architectures, examining their strengths and weaknesses. Further, we’ll analyze the key features and benefits of CIAM, including improved user experience, enhanced security, and streamlined business processes. The guide also highlights practical use cases and implementation strategies across various industries, ensuring a practical understanding of CIAM’s real-world application.
Introduction to CIAM Architecture

Source: adsttc.com
CIAM, or Customer Identity and Access Management, is a crucial component of modern digital businesses. It enables organizations to securely manage customer identities, streamline access to services, and enhance the overall customer experience. Effective CIAM solutions are vital for building trust, improving operational efficiency, and facilitating personalized interactions with customers.
A well-designed CIAM architecture provides a robust framework for managing customer identities across various touchpoints. This encompasses everything from initial registration to ongoing account management and access control. It allows for a unified view of customer data, enabling personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns.
Core Components of a CIAM System
A typical CIAM system comprises several interconnected components. These include user directories, authentication services, authorization engines, and provisioning tools. These components work in concert to manage user identities, authenticate users, grant access to resources, and provision accounts. The efficient interplay of these components ensures smooth and secure user interactions.
Types of CIAM Architectures
CIAM architectures can be deployed in various ways, catering to different organizational needs and resources.
- Cloud-based CIAM: Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and flexibility, often requiring minimal upfront investment in infrastructure. They leverage the shared resources of cloud providers, making them highly adaptable to changing business demands.
- On-premises CIAM: On-premises CIAM deployments provide greater control over data security and infrastructure. This option is typically favored by organizations with stringent regulatory compliance requirements or sensitive data needs.
- Hybrid CIAM: Hybrid deployments combine the advantages of cloud and on-premises solutions. This approach allows businesses to leverage the scalability of the cloud for certain functionalities while maintaining control over sensitive data on-premises.
Data Flow in a CIAM System
The flow of data within a CIAM system is crucial for efficient operation. A typical data flow begins with user registration or login. This triggers authentication processes that verify user credentials. Based on the verified identity, the system then determines appropriate access privileges. This data is then utilized for provisioning accounts and services tailored to the specific user.

(The diagram depicts a simplified representation of the data flow within a CIAM system, showing the sequence of events from user registration to service provisioning. Key stages include data input, authentication, authorization, and account provisioning. The diagram would visually represent the different components and their interactions.)
Roles and Responsibilities
The successful implementation of CIAM requires a well-defined structure of roles and responsibilities.
- Customer Support Representatives: Responsible for resolving customer inquiries and addressing issues related to account access and management.
- IT Administrators: Oversee the configuration, maintenance, and security of the CIAM system.
- Security Teams: Focus on protecting the system from unauthorized access and ensuring data confidentiality.
- Marketing Teams: Leverage CIAM data to personalize marketing campaigns and enhance customer engagement.
Comparison of CIAM Architecture Models
The table below summarizes the key differences between various CIAM architecture models.
| Feature | Model A (Cloud) | Model B (On-premises) | Model C (Hybrid) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud | On-premises | Hybrid |
| Scalability | High | Medium | Variable |
| Security | Robust (provider-dependent) | Moderate (organization-controlled) | Enhanced (combining aspects) |
Key Features and Benefits
CIAM, or Customer Identity and Access Management, architecture offers a robust and comprehensive approach to managing user identities and access within an organization. It streamlines authentication, authorization, and user lifecycle management, ultimately improving security and user experience. This structured approach fosters a more seamless and efficient customer journey.
The key features of CIAM are multifaceted, impacting user experience and organizational efficiency. By integrating identity management, access management, and authentication seamlessly, CIAM allows organizations to enhance their security posture while simultaneously providing a more intuitive and personalized experience for their customers. This integration results in a significant improvement in operational efficiency and user satisfaction.
Identity Management
Effective identity management is crucial for organizations to maintain accurate and up-to-date records of their users. CIAM systems facilitate user registration, profile management, and identity verification, ensuring that users have secure and personalized experiences. This meticulous approach to managing user identities reduces the risk of fraud and unauthorized access while simultaneously improving the overall user experience.
Access Management
Access management, a critical component of CIAM, determines which users have access to specific resources and applications. CIAM solutions provide granular control over access privileges, enabling organizations to restrict access based on user roles, permissions, and contextual factors. This level of control strengthens security while ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data or critical applications.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user. CIAM systems leverage various authentication methods, including password-based logins, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometric verification. This multifaceted approach ensures robust security measures, reducing the risk of unauthorized access while simultaneously providing a convenient user experience. By employing multiple authentication layers, CIAM systems create a more secure and dependable environment for users.
Advantages of Implementing a CIAM Solution
Implementing a CIAM solution offers a multitude of benefits for organizations. It improves user experience by streamlining the authentication process, enabling personalized experiences, and reducing friction in accessing services. These solutions often reduce support tickets, enhance user satisfaction, and improve the overall customer journey. This user-centric approach fosters a stronger connection between the organization and its customers.
Benefits in User Experience and Security
CIAM architectures significantly enhance user experience by providing seamless access to resources and applications. It simplifies the registration and login processes, and offers personalized experiences tailored to user preferences and needs. Simultaneously, CIAM solutions strengthen security by employing robust authentication methods, ensuring that only authorized users gain access. The combined effect of improved security and user experience translates into a stronger brand reputation and enhanced customer loyalty.
Streamlining Business Processes
CIAM solutions can streamline various business processes. For instance, they automate user onboarding, enabling faster and more efficient customer acquisition. Furthermore, by centralizing user data and providing a unified view of user interactions, organizations can gain deeper insights into customer behavior and preferences. This enhanced understanding of user interactions allows for targeted marketing campaigns, personalized recommendations, and improved service delivery.
Challenges Associated with CIAM Implementation
Implementing a CIAM solution presents some challenges. A significant challenge is the complexity of integrating CIAM with existing systems and infrastructure. Another key challenge is the need for skilled personnel to manage and maintain the system. Cost considerations also play a role, as implementing a CIAM solution can involve a substantial initial investment.
Summary Table, Ciam architecture
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Highly scalable, accommodating growing user bases and data volumes. | Complex setup requiring careful planning and configuration to ensure seamless scaling. |
| Security | Robust security features, minimizing vulnerabilities and risks. | Requires specialized personnel with expertise in security protocols and CIAM systems. |
| Cost | Potential for long-term cost savings by improving efficiency and reducing operational overhead. | Higher initial investment compared to simpler solutions, necessitating careful budgeting and planning. |
Use Cases and Implementation Strategies: Ciam Architecture
CIAM architectures offer a versatile platform for managing customer identities and access across diverse industries. Understanding the specific use cases and implementation strategies tailored to each sector is crucial for maximizing the value of CIAM. Implementing a robust CIAM strategy requires careful planning and consideration of security, scalability, and cost.
Use Cases Across Industries
CIAM applications extend beyond basic user authentication, enabling businesses to gather comprehensive customer data, personalize experiences, and streamline operations. For example, in the e-commerce sector, CIAM allows for targeted marketing campaigns, personalized recommendations, and frictionless order processing. In the financial sector, it supports secure transactions, fraud prevention, and compliance with regulatory mandates. Healthcare organizations can leverage CIAM for secure patient access to medical records and streamlined appointment scheduling. These are just a few examples of the diverse range of use cases that CIAM addresses.
Examples of Successful CIAM Implementations
Several organizations have successfully deployed CIAM solutions, demonstrating the positive impact of such strategies. A notable example is a large online retailer that implemented a CIAM solution to enhance customer experience. By centralizing user data, they significantly reduced customer support inquiries and improved conversion rates. Similarly, a leading financial institution successfully deployed CIAM to improve compliance and reduce fraud attempts. These implementations highlight the potential of CIAM to drive significant business value.
Implementation Strategies for CIAM Solutions
A successful CIAM implementation often involves a phased approach. The initial phase focuses on defining the scope of the project, identifying key stakeholders, and creating a detailed roadmap. Subsequent phases involve designing the CIAM architecture, implementing the solution, and conducting rigorous testing. A key aspect of implementation involves choosing the appropriate technology stack and integrating CIAM with existing systems.
Steps Involved in Setting Up a CIAM Architecture
The process of setting up a CIAM architecture typically involves several key steps. First, define clear objectives and goals. Next, conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems and processes to identify potential integration points. Then, select the appropriate CIAM solution, considering factors such as security, scalability, and cost. After that, the CIAM system is configured and integrated with relevant systems. Finally, thoroughly test the system and provide user training to ensure a smooth transition.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing a CIAM System
A step-by-step guide for implementing a CIAM system ensures a well-structured approach.
1. Define project goals and scope.
2. Assess existing systems and identify integration points.
3. Select and configure a CIAM solution.
4. Integrate the CIAM solution with existing systems.
5. Conduct rigorous testing and user training.
6. Monitor system performance and make necessary adjustments.
Considerations for Implementing a CIAM Solution
The successful implementation of a CIAM solution requires careful consideration of various factors. This table lists the articles’ key considerations, their descriptions, and examples.
| Consideration | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive user data is paramount. | Multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access controls. |
| Scalability | The solution should be scalable to accommodate future growth and increasing user demands. | Cloud-based solutions, modular architecture. |
| Cost | Budgetary considerations play a vital role in determining the feasibility and success of the implementation. | Cost-benefit analysis, comparing different CIAM solutions. |
Technical Aspects and Technologies
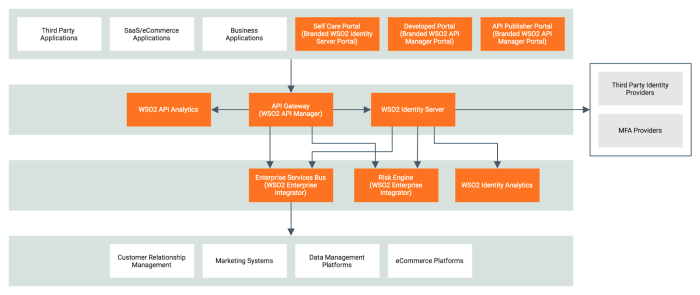
Source: thenewstack.io
CIAM architecture relies on a robust technological foundation to deliver its core functionalities. This involves carefully selected technologies for secure user authentication, data management, and integration with existing systems. Understanding these technical aspects is crucial for successful CIAM implementation.
The technical underpinnings of CIAM are multifaceted, encompassing various technologies for authentication, authorization, and data management. Effective integration with existing systems is paramount for seamless user experiences and minimal disruption to current workflows.
Technical Components of CIAM
The core components of a CIAM solution often include an API gateway, an identity provider, and a data management platform. These components work together to ensure secure and efficient user management.
- API Gateway: API gateways act as a central point of entry for all API requests. They handle authentication, authorization, and routing requests to the appropriate backend services. This centralized approach improves security and manageability. A robust API gateway is crucial for controlling access to sensitive data and ensuring consistent security protocols across different applications.
- Identity Provider (IdP): The IdP is responsible for managing user identities and authentication. It verifies user credentials, manages user roles, and provides single sign-on (SSO) capabilities. This component ensures secure access control and simplifies the user experience by reducing the need for multiple logins. A well-designed IdP facilitates secure user access to various applications and services.
- Data Management Platform (DMP): The DMP plays a vital role in storing and managing user data. It ensures data consistency, security, and accessibility. A robust DMP allows for effective data analysis and reporting, which is crucial for understanding user behavior and preferences.
Technologies Used in CIAM Solutions
Various technologies contribute to the functionality and efficiency of CIAM solutions. These technologies often include industry-standard protocols and open-source components.
- OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC): These protocols are widely used for secure authorization and authentication. They enable third-party applications to access user data securely without directly handling sensitive credentials. Their use in CIAM facilitates secure access to resources across different applications.
- REST APIs: REST APIs are commonly employed for communication between different components of a CIAM solution. Their use promotes flexibility and interoperability. This allows different parts of the CIAM system to communicate efficiently, enabling seamless data exchange.
- Cloud Computing Platforms: Cloud-based platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are increasingly used for CIAM implementations. These platforms offer scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based solutions can help businesses easily manage and scale their CIAM infrastructure.
CIAM Platforms and Tools
Several CIAM platforms and tools are available, offering different features and functionalities. Choosing the right platform depends on the specific needs of the organization.
- Examples of CIAM Platforms: Several companies offer comprehensive CIAM platforms, each with its own set of features. These platforms usually include user management, authentication, and authorization capabilities. Choosing a platform depends on factors such as budget, scalability requirements, and specific functionalities.
Integration with Other Systems
CIAM solutions are often integrated with existing enterprise systems. This seamless integration ensures that user data is readily available and consistent across various applications. Integration with existing systems is crucial for smooth workflow transitions.
- Integration Strategies: Common integration strategies include using APIs, message queues, and middleware solutions. The selected approach depends on the existing infrastructure and the specific integration requirements.
Comparison of CIAM Technologies
Different CIAM technologies offer varying levels of security, scalability, and flexibility. Organizations must evaluate these factors when choosing a CIAM solution.
- Key Considerations: When evaluating different technologies, consider factors such as security protocols, data management capabilities, and scalability. A thorough evaluation helps in choosing a CIAM solution that meets specific business requirements.
Technology Overview Table
| Technology | Description | Use Case ||—|—|—|| API Gateway | Manages API requests | Secure API access || Identity Provider | Manages user identities | Single sign-on || Data Management Platform | Stores and manages data | User data storage || OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect | Secure authorization and authentication | Secure access to resources || REST APIs | Facilitates communication between components | Data exchange between systems || Cloud Computing Platforms | Scalable and reliable infrastructure | Deployment and management of CIAM solutions |
Security Considerations and Best Practices

Source: adsttc.com
CIAM systems, while offering significant advantages, are susceptible to various security threats. Robust security measures are crucial to protect user data, maintain system integrity, and uphold user trust. Implementing comprehensive security strategies from the design phase is paramount to mitigate risks effectively.
Effective security in CIAM involves a multi-layered approach that incorporates strong authentication mechanisms, data encryption, and regular security audits. A proactive stance toward security is essential to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
Security Implications of CIAM Architecture
CIAM systems, by their nature, collect and process sensitive user data, including personal information, login credentials, and transaction details. Compromising this data can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications. The interconnected nature of CIAM systems also introduces potential vulnerabilities if one component is compromised. Data breaches can have far-reaching effects on businesses and users alike.
Best Practices for Securing a CIAM System
Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect user data and maintain system integrity. These measures should be designed from the outset, incorporating strong authentication, secure data storage, and regular security assessments. Regular security updates and patches are vital to address vulnerabilities as they emerge.
- Strong Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for unauthorized users to access accounts. Strong passwords, ideally generated and managed by the system, contribute to the overall security posture. Regular password audits and updates further strengthen this aspect.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest is paramount. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key. This practice is essential for maintaining data confidentiality.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits, including penetration testing, helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system. Proactive identification of potential risks allows for timely remediation, preventing exploitation.
Importance of Data Privacy and Compliance
Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, dictate how organizations handle personal data. CIAM systems must comply with these regulations to avoid legal repercussions. Maintaining user trust is essential, and demonstrating compliance with data privacy regulations builds confidence and fosters trust.
- Data Minimization: Only collect the data necessary for the intended purpose. Collecting excessive data increases the attack surface and potentially leads to breaches. Regular reviews of data collection practices help to ensure compliance and minimize risks.
- Data Subject Rights: Ensuring users have the ability to access, correct, and delete their data is critical for complying with data privacy regulations. Clear mechanisms to support these rights are essential.
Different Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
CIAM systems face a range of security threats, including phishing attacks, SQL injection vulnerabilities, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Understanding these threats allows for proactive mitigation strategies. Insider threats from malicious or negligent employees also pose a significant risk.
- Phishing Attacks: Sophisticated phishing attacks attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials. Robust security awareness training and email filtering are essential defenses.
- SQL Injection: Malicious code injected into SQL queries can compromise database integrity and potentially leak sensitive data. Prepared statements and input validation are crucial safeguards.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): XSS vulnerabilities allow attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. Output encoding and input validation are vital for mitigating this risk.
Strategies for Mitigating Security Risks
Implementing a multi-layered security approach is vital for mitigating security risks effectively. Regular security updates, strong access controls, and robust incident response plans are essential elements of this strategy. Security awareness training for employees is critical to prevent human error.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs, providing insights into potential threats and vulnerabilities. Real-time threat detection and response capabilities are critical.
- Vulnerability Management: Proactive identification and remediation of vulnerabilities are essential. Automated vulnerability-scanning tools and regular penetration testing contribute to this effort.
- Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan Artikels procedures for handling security breaches. This includes containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis.
Checklist for Implementing Security Measures in a CIAM System
A comprehensive checklist ensures that all security measures are implemented correctly. This checklist should be reviewed and updated regularly to address evolving threats and vulnerabilities. Regular security assessments are essential for continuous improvement.
- Conduct a thorough security risk assessment.
- Implement strong authentication mechanisms (e.g., MFA).
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit.
- Regularly update and patch the system.
- Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
- Establish and maintain an incident response plan.
- Implement robust access controls.
- Train employees on security best practices.
- Comply with relevant data privacy regulations.
Future Trends and Developments
CIAM architecture is constantly evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of digital transformation and customer expectations. This evolution is driven by emerging technologies, shifting business needs, and a growing focus on personalized experiences. Understanding these trends is crucial for organizations looking to stay ahead of the curve and leverage the full potential of CIAM.
Emerging Trends in CIAM
CIAM is evolving beyond its initial focus on customer onboarding and identity management. The future will see a greater emphasis on seamless and personalized experiences across all customer touchpoints. This includes leveraging advanced analytics to understand customer behavior and preferences, facilitating personalized interactions, and providing proactive support. Furthermore, a shift toward automation and AI-powered solutions will be increasingly important in streamlining processes and improving efficiency.
Future Developments in CIAM
Several key areas are expected to see significant advancements in CIAM. These include:
- AI-powered personalization: Machine learning algorithms will play a more prominent role in tailoring customer experiences. This will involve dynamic content adaptation, personalized recommendations, and proactive service delivery based on individual customer profiles and behaviors. For example, a retailer could use AI to recommend products based on past purchases and browsing history, creating a more engaging and relevant shopping experience.
- Enhanced Security Measures: The rising threat of cyberattacks necessitates continuous improvements in security measures within CIAM. This includes implementing advanced authentication methods, such as biometrics and multi-factor authentication, and robust data encryption techniques. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and threat detection mechanisms are essential to protect customer data and maintain system integrity.
- Integration with other platforms: CIAM solutions will increasingly integrate with other enterprise systems, such as CRM, marketing automation, and commerce platforms. This seamless integration will enable a unified view of the customer across all touchpoints, leading to more efficient and personalized interactions.
- Contextual Awareness: Future CIAM systems will increasingly understand the context of a customer’s interaction. This will involve gathering information from various sources, including device type, location, and time of day, to provide a more personalized and relevant experience. For instance, a banking app could offer different features based on whether the customer is at home or in a branch or whether they are checking their account in the morning or evening.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on CIAM
Emerging technologies are reshaping the CIAM landscape, offering new opportunities, nd presenting unique challenges. The integration of blockchain technology, for instance, could improve data security and transparency, while the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents new opportunities for identity management and personalized experiences in various sectors.
Evolution of CIAM in the Coming Years
CIAM will evolve from a primarily back-end system to a more integrated, customer-centric platform. This will involve a greater focus on user experience, personalized interactions, and seamless integration with other business systems. Organizations need to anticipate and adapt to these evolving trends to maximize the value of their CIAM initiatives.
Challenges and Opportunities Associated with Future CIAM Developments
The future of CIAM presents both challenges and opportunities. Addressing security concerns, ensuring data privacy, and managing the complexities of integrating various technologies will be key challenges. However, the opportunities for creating more personalized and engaging customer experiences, streamlining business processes, and enhancing customer loyalty are substantial. Successfully navigating these challenges will be crucial for organizations looking to remain competitive in the future.
Final Summary
In conclusion, CIAM architecture offers a powerful solution for managing identities and access in today’s digital landscape. Its diverse deployment models, robust security features, and potential for streamlining business processes make it an attractive option for organizations. While challenges like complex setup and high initial investment exist, the potential benefits in terms of scalability, security, and user experience often outweigh the drawbacks. The future of CIAM appears promising, with ongoing developments likely to enhance its capabilities and address existing challenges. Understanding the nuances of CIAM architecture is crucial for organizations seeking to leverage its potential to improve security, user experience, and business operations.