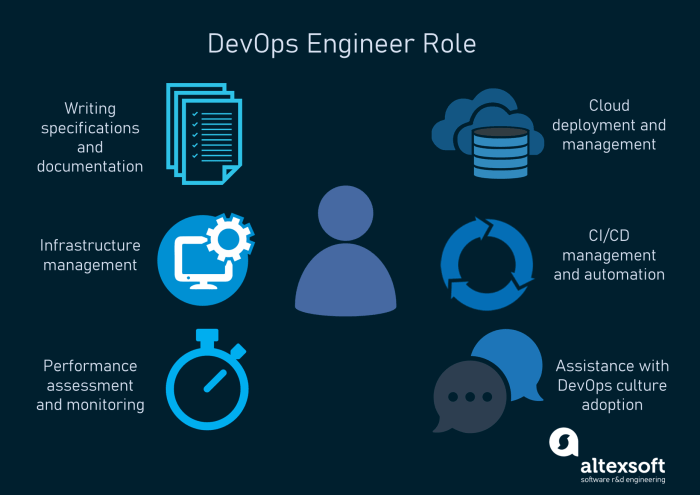
AWS DevOps Architect A Deep Dive
AWS DevOps Architect is a critical role in today’s cloud-driven world. This role demands a deep understanding of AWS services, a proficiency in automation, and a commitment to building robust, scalable, and secure cloud infrastructure. The architect designs and implements DevOps solutions, focusing on continuous integration and delivery pipelines to streamline software deployment and maintenance.
This exploration delves into the core responsibilities, essential skills, and future trends shaping this crucial cloud profession. We’ll examine the distinct differences between DevOps engineers and architects, highlighting the unique challenges and rewards of this career path.
Defining the Role
An AWS DevOps Architect plays a crucial role in designing, implementing, and managing robust and scalable cloud infrastructure using Amazon Web Services (AWS). This involves a deep understanding of AWS services and the ability to apply DevOps principles to automate and streamline the entire software development lifecycle. They bridge the gap between development and operations, fostering collaboration and efficiency within organizations.
The primary focus is on creating solutions that are reliable, secure, and cost-effective. This includes designing and implementing infrastructure as code (IaC), automating deployments, and ensuring continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. Their expertise extends to various aspects of cloud computing, from networking and security to databases and storage.
Role Definition
An AWS DevOps Architect is a senior-level professional responsible for designing and implementing end-to-end cloud solutions using AWS. Their expertise spans the entire software development lifecycle, from initial design to deployment and ongoing maintenance. They are accountable for ensuring the stability, scalability, and security of the cloud infrastructure.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
The duties of an AWS DevOps Architect encompass a broad range of activities. These include:
- Designing and implementing robust and scalable cloud infrastructure using AWS services.
- Automating deployments and infrastructure provisioning using tools like AWS CloudFormation, Terraform, or similar.
- Establishing and maintaining CI/CD pipelines for seamless software delivery.
- Implementing and maintaining security best practices for the cloud infrastructure.
- Monitoring and optimizing cloud resource utilization for cost-effectiveness.
- Troubleshooting and resolving infrastructure issues.
- Collaborating with development, operations, and security teams to ensure smooth communication and alignment.
These responsibilities highlight the multifaceted nature of the role, requiring a combination of technical expertise and leadership skills.
AWS DevOps Architect vs. AWS DevOps Engineer
While both roles work with AWS and DevOps principles, their responsibilities and skill sets differ significantly. An AWS DevOps Engineer focuses on implementing and maintaining the infrastructure, whereas an AWS DevOps Architect is more focused on designing and strategizing the overall solution.
- An AWS DevOps Engineer focuses on the practical application of AWS services and DevOps methodologies. They often have more hands-on experience with specific tools and technologies.
- An AWS DevOps Architect has a broader perspective, encompassing strategic planning, architecture design, and overall solution optimization. They emphasize the long-term vision and impact of their work.
Skills and Experience
The required skills and experience for each role differ based on their respective responsibilities.
| Skill/Experience | AWS DevOps Engineer | AWS DevOps Architect |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Services | Proficient in core AWS services | Deep understanding of a wide range of AWS services |
| DevOps Tools | Proficient in specific DevOps tools | Expertise in various DevOps tools and methodologies |
| Design and Architecture | Limited design responsibilities | Significant design and architecture skills |
| Problem-solving | Problem-solving within existing frameworks | Problem-solving across the entire system |
| Leadership | Minimal leadership requirements | Strong leadership and communication skills |
Career Path
A typical career path for an AWS DevOps Architect often involves a progression from an AWS DevOps Engineer role. Gaining hands-on experience with AWS services, DevOps methodologies, and cloud architecture design are essential steps in this progression. Building a strong portfolio showcasing practical implementations and leadership roles will be key to career advancement. Further certifications and continuous learning in the field are also crucial.
Core Skills and Knowledge

Source: venturejolt.com
A successful AWS DevOps Architect requires a strong foundation in cloud computing principles, coupled with practical expertise in AWS services and tools. This deep understanding allows them to design, implement, and manage robust and scalable cloud infrastructure solutions. They are adept at automating processes, ensuring security, and optimizing resource utilization.
Essential Technical Skills
A robust skill set is critical for an AWS DevOps Architect. This includes proficiency in various programming languages, a strong understanding of infrastructure as code (IaC), and cloud security best practices. Hands-on experience with automation tools and scripting languages is essential for effective and efficient cloud deployments.
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in languages like Python, Java, or Go is highly beneficial. These languages are frequently used for scripting, automation, and building custom solutions within the AWS ecosystem. Experience with at least one language allows architects to create and maintain custom scripts for automating tasks and implementing complex solutions.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): A deep understanding of IaC principles, such as using tools like AWS CloudFormation or Terraform, is crucial. This enables the creation and management of infrastructure through code, ensuring consistency, reproducibility, and efficiency. This approach is key to automating infrastructure provisioning and modification.
- Cloud Security: Implementing and maintaining robust security measures across the cloud infrastructure is paramount. Knowledge of security best practices, including access control, encryption, and vulnerability management, is essential. Adherence to these principles safeguards sensitive data and prevents unauthorized access.
Proficiency in AWS Services and Tools
An AWS DevOps Architect should be well-versed in a wide array of AWS services. This proficiency enables the design and implementation of efficient and scalable solutions.
- Compute Services: Deep familiarity with EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), Lambda, and other compute services allows architects to provision and manage virtual servers and serverless functions. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of these services is key to selecting the optimal solution for specific needs.
- Storage Services: Proficiency with S3 (Simple Storage Service), EBS (Elastic Block Store), and other storage services enables the architect to design robust storage solutions for various application requirements. An understanding of appropriate storage options for different workloads is essential.
- Networking Services: Knowledge of VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), Route 53, and other networking services is crucial for designing secure and scalable network configurations. This ensures the proper communication and access between different components within the cloud environment.
- Database Services: Familiarity with RDS (Relational Database Service), DynamoDB, and other database services allows architects to choose the right database for specific applications. This understanding is critical for ensuring the proper performance and scalability of database solutions.
- Management Tools: Experience with tools like CloudWatch, X-Ray, and others for monitoring, logging, and troubleshooting is critical. Effective monitoring is crucial for identifying and resolving issues quickly.
Importance of Cloud Security Principles
Cloud security is a critical aspect of any cloud-based architecture. AWS DevOps Architects must prioritize security throughout the design and implementation process.
Security is not an afterthought; it is an integral part of the design process.
Implementing robust security measures ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and resources.
- Access Control: Implementing strict access control mechanisms through IAM (Identity and Access Management) is essential. This controls who has access to what resources, limiting potential risks.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit protects sensitive information. This practice is critical for maintaining compliance with industry regulations and best practices.
- Vulnerability Management: Proactively identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities is crucial. This ensures the security of the infrastructure and applications.
Understanding Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Principles
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a core concept in modern cloud deployments. It allows for repeatable, consistent, and automated infrastructure management.
- Automation: IaC automates the provisioning and management of infrastructure, leading to reduced errors and faster deployments.
- Version Control: Using version control systems like Git for IaC code enables tracking changes, managing different versions, and facilitating collaboration.
- Consistency: IaC ensures that infrastructure is consistently deployed across different environments, promoting reliability and reducing deployment errors.
Necessity of Automation and Scripting Skills
Automation and scripting skills are essential for an AWS DevOps Architect. These skills enable the creation of repeatable and reliable processes.
- Automation Tools: Utilizing tools like AWS CLI, CloudFormation, and Terraform to automate tasks is critical. This significantly reduces manual effort and human error.
- Scripting Languages: Programming languages like Python or PowerShell are essential for creating custom scripts to automate various tasks, from deploying applications to managing resources.
- Efficiency: Automation improves efficiency by reducing manual effort and enabling faster deployments. This allows teams to focus on higher-level tasks.
Design Principles and Practices: AWS DevOps Architect
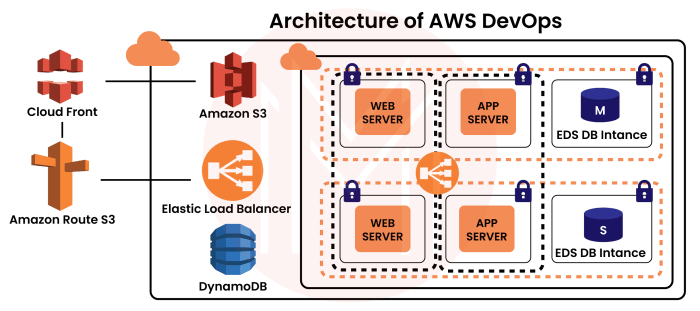
Source: mindmajix.com
Designing a robust and scalable AWS infrastructure requires a thoughtful approach that prioritizes efficiency, security, and maintainability. A well-designed AWS architecture should anticipate future growth and adapt to changing business needs. This necessitates a clear understanding of various deployment models, continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, and effective monitoring strategies.
A strong foundation in design principles ensures that the architecture can support increasing workloads and evolving requirements without compromising performance or security. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and facilitates smooth transitions during upgrades or scaling events.
Robust and Scalable AWS Infrastructure Architecture
A robust and scalable AWS infrastructure for a fictional company, “InnovateTech,” might employ a multi-region architecture. This strategy distributes data and applications across multiple availability zones within different geographic regions. This approach improves resilience to outages and enhances disaster recovery capabilities. Data backups and replication are crucial components, ensuring business continuity. Key considerations include selecting appropriate instance types based on predicted workloads and employing auto-scaling groups to adjust resources dynamically.
High-Level Architecture Diagram for an AWS DevOps Solution
The high-level architecture for an AWS DevOps solution for InnovateTech would involve a layered approach. The foundational layer comprises compute resources, storage, and networking components. The middle layer encompasses CI/CD pipelines, automated deployments, and infrastructure as code (IaC). The top layer features monitoring and logging services to track performance and identify potential issues. A central role would be played by a managed identity and access management (IAM) service. Visualizing this architecture using diagrams, such as CloudFormation templates, is essential for clarity and understanding.
AWS Deployment Models
Different deployment models cater to various needs and environments. InnovateTech might utilize a combination of deployment models.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): IaC enables automated provisioning and management of infrastructure, minimizing manual errors and enhancing consistency. Tools like AWS CloudFormation and AWS CDK allow for declarative infrastructure definition, facilitating reproducibility and version control. This approach streamlines deployments and reduces the risk of human error in configurations.
- Serverless Computing: InnovateTech can leverage serverless computing services like AWS Lambda and API Gateway for functions that require low-latency responses and flexible scaling. This strategy optimizes cost efficiency by paying only for consumed resources. The absence of server management tasks reduces operational overhead.
- Containerization: Containerization using Docker and Kubernetes orchestrates containerized applications, ensuring consistency across environments. This approach enables fast deployments, scalability, and efficient resource utilization. Using container orchestration like ECS or EKS further streamlines container management and deployment.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Pipelines, Aws devops architect
CI/CD pipelines automate the software development lifecycle from code integration to deployment. They reduce manual intervention, leading to faster release cycles and improved code quality. For InnovateTech, this means integrating code changes frequently, automatically testing the code, and automating the deployment process to various environments, including development, testing, and production. This automation minimizes errors and accelerates delivery.
Best Practices for Managing and Monitoring AWS Infrastructure
Effective management and monitoring of AWS infrastructure are critical for maintaining service availability and security.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry best practices and regulatory requirements. Tools like AWS Security Hub and GuardDuty are essential in identifying and mitigating threats.
- Logging and Monitoring: Implementing robust logging and monitoring solutions allows for real-time tracking of resource utilization, performance metrics, and potential issues. CloudWatch provides comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities.
- Version Control: Employing version control systems for infrastructure code ensures that changes are tracked, allowing for rollback capabilities and easy management of different configurations. Git is often used for this purpose.
Tools and Technologies
AWS DevOps Architects leverage a diverse range of tools and technologies to streamline application development, deployment, and management. This encompasses a spectrum of services, from Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools to CI/CD pipelines and monitoring solutions. Effective utilization of these tools is crucial for automating tasks, ensuring consistency, and fostering rapid iteration within AWS environments.
Popular DevOps Tools Integrated with AWS
Various DevOps tools seamlessly integrate with AWS services, offering robust capabilities for automating tasks and managing deployments. These tools empower architects to orchestrate complex processes, ensuring efficient and reliable workflows. Key tools include:
- AWS CodePipeline: A fully managed continuous delivery service that enables automated build, test, and deployment processes within AWS. It allows for integration with various AWS services and third-party tools.
- AWS CodeBuild: A fully managed build service that compiles source code, runs tests, and packages applications. It integrates seamlessly with CodePipeline for automated build processes.
- AWS CodeDeploy: A deployment service that automates the deployment of applications and infrastructure changes to various AWS environments. It simplifies deployments across different AWS services.
- AWS CloudFormation: A powerful IaC tool that allows architects to define and provision AWS resources through declarative templates. This ensures consistency and repeatability in infrastructure deployments.
- Terraform: A popular open-source IaC tool that can be used with AWS to define and manage infrastructure. It allows for complex infrastructure configurations and deployments, offering flexibility for non-AWS resources.
- Ansible: A configuration management and automation tool that automates tasks across various systems, including AWS instances. It can be used to configure and deploy applications within AWS.
- Jenkins: A widely used open-source automation server that can integrate with AWS services for CI/CD pipelines. It provides flexibility and customizability for building complex automation workflows.
Comparison of CI/CD Tools in AWS
CI/CD tools in AWS environments offer varying degrees of automation and integration capabilities. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific needs and complexity of the project.
- AWS CodePipeline: A managed service that provides a visual workflow for defining and managing CI/CD pipelines. It offers ease of use and a strong integration with other AWS services, but its configuration might be less flexible compared to other options.
- Jenkins: An open-source tool that can be deployed and configured on AWS EC2 instances. It provides significant customization options but requires management overhead and careful configuration to integrate with AWS services effectively.
Strengths and Weaknesses of AWS Services for DevOps
A table outlining the strengths and weaknesses of various AWS services for DevOps purposes can provide a comparative analysis of their functionalities and limitations.
| AWS Service | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| AWS CodePipeline | Fully managed, easy integration with other AWS services, visual pipeline management | Limited customization options compared to Jenkins |
| AWS CodeDeploy | Automated deployments across various environments, implifies deployments | Might not be ideal for complex deployments with diverse configurations |
| AWS CloudFormation | Declarative infrastructure definition, repeatable deployments, easy management of infrastructure as code | Requires expertise in defining templates for complex deployments |
| EC2 | Provides flexibility in selecting operating systems and configurations, supports various use cases | Requires manual configuration and management, can be complex for large-scale deployments |
Use Cases for AWS Services
Specific AWS services play critical roles in different DevOps scenarios. Understanding these use cases is essential for effective implementation.
- AWS CodePipeline: Suitable for automating deployments of applications to various AWS environments, ensuring consistency and repeatability. Examples include automating deployments of web applications, microservices, and serverless functions.
- AWS CodeDeploy: Ideal for automating the deployment of applications and infrastructure changes across multiple environments. Use cases include rolling deployments, blue/green deployments, and canary deployments.
- AWS CloudFormation: Crucial for defining and provisioning AWS resources in a declarative manner. Examples include automating the creation of development, testing, and production environments, and provisioning databases and load balancers.
Industry Trends and Future Prospects
The AWS DevOps Architect role is rapidly evolving, driven by the constant advancements in cloud computing and the increasing complexity of modern applications. This evolution demands a nuanced understanding of emerging technologies, a proactive approach to automation, and a focus on robust security practices. This section delves into the current trends and future outlook for this crucial role.
The demands on AWS DevOps Architects are continuously shifting, requiring a proactive approach to adapting to new technologies and skillsets. This dynamic environment necessitates a focus on continuous learning and the acquisition of new competencies to remain competitive and relevant.
Latest Trends in AWS DevOps Architect Roles
AWS DevOps Architects are increasingly expected to have a deep understanding of serverless computing, containerization, and microservices architectures. This reflects the trend towards building more scalable, resilient, and cost-effective applications in the cloud. The ability to design and implement automated CI/CD pipelines is becoming table stakes, and there is a corresponding increase in the use of managed services to simplify deployments and maintenance.
Emerging Technologies Impacting the Field
Several emerging technologies are shaping the future of AWS DevOps. Serverless functions, leveraging services like AWS Lambda, are gaining traction for their cost-effectiveness and ability to scale dynamically. The adoption of container orchestration platforms, such as Kubernetes, is also on the rise, enabling more efficient deployment and management of containerized applications. This shift toward containerization and microservices architecture further necessitates robust monitoring and logging capabilities to maintain application health.
Future Demands and Skills Required for AWS DevOps Architects
The future demands for AWS DevOps Architects will encompass a broader skill set beyond just cloud infrastructure management. Proficiency in serverless architectures, containerization technologies (especially Kubernetes), and the ability to design and implement secure CI/CD pipelines will be crucial. Furthermore, a strong understanding of data analytics, machine learning, and AI will be valuable for optimizing application performance and identifying potential issues proactively. Experience with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools is paramount, as is proficiency in scripting languages like Python or PowerShell.
Evolving Role of Automation and AI in DevOps
Automation is transforming the DevOps landscape. AWS DevOps Architects are now expected to leverage automation tools and techniques to streamline tasks, reduce manual intervention, and ensure faster delivery cycles. AI is increasingly integrated into DevOps processes, allowing for predictive analysis, proactive issue identification, and intelligent resource allocation. This shift toward automation and AI will continue to drive efficiency and reduce human error in the development lifecycle.
Increasing Need for Security Expertise in AWS DevOps Roles
Security is a paramount concern in the cloud environment. AWS DevOps Architects need to possess a strong understanding of security best practices and compliance standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR. This includes expertise in implementing security measures at every stage of the application lifecycle, from infrastructure design to deployment and operation. A proactive approach to security, incorporating security testing and vulnerability assessments into the CI/CD pipeline, is becoming an integral part of the role.
Practical Examples and Scenarios

Source: proitacademy.in
AWS DevOps Architects are crucial in modern software development, bridging the gap between development and operations. They ensure seamless deployment, efficient resource management, and reliable systems through automation and optimization. Their expertise is vital in today’s complex cloud environments.
Real-world scenarios frequently demand a DevOps Architect’s skills. From migrating legacy applications to the cloud to automating complex deployments and improving application performance, their expertise is highly sought after.
Real-World Scenario Requiring an AWS DevOps Architect
A large e-commerce company experiences significant performance issues during peak shopping seasons. Orders are delayed, and customer satisfaction plummets. An AWS DevOps Architect would be needed to analyze the bottlenecks, identify areas for improvement, and implement solutions to enhance scalability and resilience. This might include optimizing database queries, implementing load balancing across multiple AWS regions, and automating infrastructure provisioning to meet demand fluctuations.
Case Study of a Successful AWS DevOps Implementation
A software company migrated its entire infrastructure to AWS, resulting in a 30% reduction in operational costs and a 20% increase in deployment speed. This success was achieved through a well-defined DevOps strategy implemented by an AWS DevOps Architect. The strategy included automation of infrastructure provisioning, continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, and a robust monitoring and alerting system. Key improvements involved standardized deployment processes, improved communication between development and operations teams, and increased efficiency.
Problem Statement Solved by an AWS DevOps Architect
A company’s microservices architecture, deployed on AWS, experiences inconsistent performance across different environments. The DevOps Architect would investigate the root cause, identifying discrepancies in configuration and deployment across development, staging, and production environments. They would then design and implement solutions to ensure consistent performance and reliability across all environments, including standardizing deployment procedures and automated testing.
Hypothetical Scenario: Troubleshooting an Issue
An AWS DevOps Architect is tasked with resolving an unexpected outage affecting a critical application deployed on AWS. The application experiences intermittent failures, and logs indicate potential issues with network connectivity. The architect would employ various troubleshooting techniques, including examining network configurations, analyzing cloud logs, and checking resource utilization. They would likely use tools like AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch to pinpoint the cause of the outage and implement corrective measures.
Designing a Monitoring and Alerting System in AWS for DevOps
A robust monitoring and alerting system is essential for maintaining application health and ensuring service availability. The AWS DevOps Architect would design a system using CloudWatch, a comprehensive monitoring service. Key components include metrics collection from EC2 instances, load balancers, and databases. Alerts are configured for critical thresholds, triggering notifications to relevant teams. This proactive approach ensures swift response to potential issues and minimizes downtime. The system would include dashboards for visualizing key metrics, providing a holistic view of application performance. The design would ensure scalability and flexibility to accommodate future growth and changes in the application.
Job Market and Compensation
The AWS DevOps Architect job market is robust and consistently shows high demand. This demand stems from the increasing adoption of cloud computing and the need for skilled professionals to manage and optimize cloud infrastructure. Competition for these roles is also present, but successful candidates typically possess a strong understanding of AWS services, demonstrable experience, and relevant certifications.
The salary for AWS DevOps Architects varies significantly based on experience, location, and specific responsibilities. Compensation packages often include competitive base salaries, potentially substantial performance-based bonuses, and benefits like health insurance and retirement plans.
Current Job Market Trends
The AWS DevOps Architect job market is experiencing healthy growth, with companies actively seeking professionals with the skills to design, implement, and maintain cloud-based solutions. Job postings frequently highlight the need for expertise in areas like infrastructure as code, automation, security, and monitoring within the AWS ecosystem. This indicates a sustained demand for this role across various sectors.
Salary Ranges
Compensation for AWS DevOps Architects is influenced by several factors. Entry-level positions typically fall within a certain range, while more senior architects with extensive experience and proven track records command higher salaries. Location also plays a significant role, with roles in major tech hubs often commanding higher compensation.
- Entry-level (0-2 years experience): $80,000 – $120,000 annually
- Mid-level (3-5 years experience): $120,000 – $160,000 annually
- Senior-level (6+ years experience): $160,000 – $200,000+ annually
These ranges are approximate and can vary based on specific skill sets, employer, and location. For example, a senior architect specializing in highly specialized AWS services may command a salary outside of this range.
Career Progression Opportunities
AWS DevOps Architects have numerous career progression opportunities. They can advance into leadership roles, such as cloud engineering manager or DevOps manager. Alternatively, they can specialize in specific areas, like security or automation, gaining expertise in niche technologies. They may also move into architecting solutions for entirely different business units or industries.
Industry-Specific Role Comparison
The responsibilities of an AWS DevOps Architect can differ across various industries, even if the core skills remain consistent.
| Industry | Specific Responsibilities | Example Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Ensuring high availability and security for critical financial systems | Compliance, regulatory requirements, and data security |
| Healthcare | Implementing secure and compliant cloud solutions for patient data management | HIPAA compliance, data privacy, and patient record management |
| Retail | Optimizing e-commerce platforms and supply chain management through automation | Scalability, high availability, and order fulfillment automation |
| Manufacturing | Automating production processes and improving operational efficiency | Supply chain optimization, real-time data analysis, and machine learning integration |
This table highlights some potential industry-specific nuances in the roles of AWS DevOps Architects.
Required Certifications
AWS certifications play a crucial role in validating the skills and knowledge of DevOps Architects. These certifications demonstrate proficiency in various AWS services and practices, enhancing employability and career progression.
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer – Professional
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate
These certifications, along with practical experience, form a strong foundation for a successful career in this field.
Summary
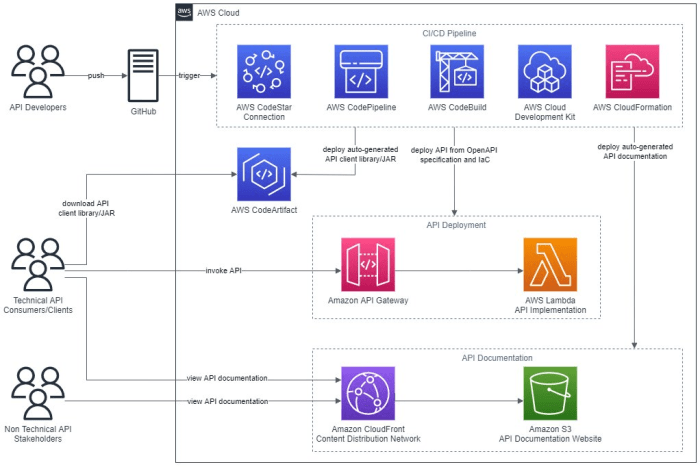
Source: cloudfront.net
In conclusion, the AWS DevOps Architect role is dynamic and in high demand. Success hinges on mastering cloud technologies, embracing automation, and understanding security principles. The future of this role is intertwined with emerging technologies like AI and the ongoing evolution of cloud infrastructure, demanding adaptability and continuous learning. This role is vital for organizations looking to optimize their cloud deployments and gain a competitive edge in the market.